Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 18, №7, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Клінічне спостереження рідкісного випадку збереження нижньої кінцівки після перев’язки основних стовбурів стегнової артерії та вени завдяки колатеральному кровообігу у наркозалежного пацієнта на фоні вкрай тяжкої анемії і використання цього спостереження в проведенні практичних занять при підготовці лікарів загальної практики — сімейної медицини
Авторы: Рудіченко В.М. (1), Рейзін Д.В. (2), Рейзін В.І. (2), Соколенко А.Л. (1)
(1) — Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
(2) — Київська міська клінічна лікарня № 8, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
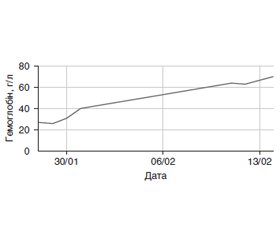
Потяг до хімічних речовин (препаратів, англ. — substance addiction) та залежність від них, включно з курінням, алкоголем та незаконним застосуванням препаратів (англ. — illicit drugs), є прямо або опосередковано відповідальними за кількість смертей кожного року у світі, яка вища, ніж кількість смертей від раку, та вважаються причиною однієї п’ятої частини всіх смертей у світі. Лікувальні можливості часто обмежені та недостатньо адекватні, рецидиви у пролікованих часті. Шляхи, які призводять до потягу та залежності, є комплексними та багатовимірними і містять відмінності в молекулярній та генетичній експресії, порушення мозкової чутливості до стимулів, які стосуються винагородження та стресу, та поведінкові особливості, які залучають сприйняття ризику, соціальну ізоляцію та/або стресорну дисрегуляцію. Низка країн проводить регулярні зрізові популяційні дослідження щодо незаконного застосування препаратів та пов’язаних розладів. У статті наведено власне клінічне спостереження рідкісного випадку збереження кінцівки після перев’язки основних стовбурів стегнової артерії та вени завдяки колатеральному кровообігу у наркозалежного пацієнта на фоні вкрай тяжкої анемії. Матеріали цього випадку вважаємо демонстративними для обговорення та широко застосовуємо під час практичних занять як державною, так і англійською мовами на додипломному та післядипломному етапах підготовки лікарів загальної практики — сімейної медицини.
Substance addiction, which includes tobacco smoking, alcohol consumption and using of illicit drugs, are indirectly or directly responsible for the number of annual deaths worldwide, which is higher than that of due to cancer and is considered to be the cause of one fifth of all deaths in the world. Treatment possibilities very often are limited and not sufficient, relapses are common. Ways of appearing of substance addiction are complex and multidirectional, and include the differences in molecular and genetical expressions, altered brain sensitivities to stimuli, which are connected to rewarding and stress, and behavioural features, which include admittance of the risks, social isolation and/or stress dysregulation. Some countries perform regular cross-sectional population studies of illegal drug using and associated disorders. Article describes own clinical observation of a rare case of saving lower extremity after ligation of main trunks of the femoral artery and vein as a consequence of collateral circulation in a drug addict on the background of severe anemia. We consider the materials of this case to be demonstrative for discussion and widely use them during practical classes in both the state and English languages at the undergraduate and postgraduate stages of training general practitioners — family physicians.
потяг до наркотичних речовин; залежність від наркотичних речовин; наркозалежний пацієнт; ін’єкційна наркоманія
substance addiction; substance dependence; drug addict; injection drug use
/7/48.jpg)
/7/51_2.jpg)
Висновки
- Рейзін В.І., Рудіченко В.М., Хантіль Н.М. Моніторинг стану та лікування хворого з верифікованим гепатитом С із ускладненнями: власні клінічні спостереження. Ліки України. 2018. № 4. С. 24-29.
- Рудіченко В.М. Он-лайн сайти у викладанні англійською мовою в підготовці лікарів загальної практики — сімейної медицини на додипломному та післядипломному етапах. Мат-ли наук.-практ. конф. з міжнар. участю «Щорічні терапевтичні читання. Неінфекційні захворювання: профілактика та зміцнення здоров’я в Україні», Харків, 22–23 квітня 2021 р. За ред. Г.Д. Фадєєнко та ін. Харків, 2021. С. 119. Режим доступу: https//therapy.org.ua/files/tezu_22_04_2021.pdf.
- Amaral D.G., Dent J.A. Development of the mossy fibers of the dentate gyrus: I. A light and electron microscopic study of the mossy fibers and their expansions. J. Comp. Neurol. 1981. 195. 51-86.
- The enduring effects of abuse and related adverse experiences in childhood. A convergence of evidence from neurobiology and epidemiology. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2006. 256. 174-186.
- Bales K.L., Perkeybile A.M. Developmental experiences and the oxytocin receptor system. Horm. Behav. 2012. 61. 313-319.
- Barth R.P. Preventing child abuse and neglect with parent training: evidence and opportunities. Fut. Child. 2009. 19. 95-118.
- Bayer S.A. et al. Time of neuron origin and gradients of neurogenesis in midbrain dopaminergic neurons in the mouse. Exp. Brain Res. 1995. 105. 191-199.
- Burke R.E. Ontogenic cell death in the nigrostriatal system. Cell Tis. Res. 2004. 318. 63-72.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Excessive drinking costs US $2235 billion. 2014.
- Chang K.C., Wang J.D., Saxon A. et al. Causes of death and expected years of life lost among treated opioid dependent individuals in the United States and Taiwan. Int. J. Drug. Policy. 2017. 43. 1-6.
- Child Welfare Information Gateway. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services & Children’s Bureau. Parental substance use and the child welfare system. Washington, DC, 2014.
- Dube S.R. et al. Childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction and the risk of illicit drug use: the adverse childhood experiences study. Ped. 2003. 111. 564-572.
- Kim S., Kwok S., Mayes L.C. et al. Early adverse experience and substance addiction: dopamine, oxytocin, and glucocorticoid pathways. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2017. 1394. 74-91.
- Kraus L., Piontek D., Atzendorf J., Gomes de Matos E. Zeitliche Entwicklungen im Substanzkonsum in der deutschen Allgemeinbevölkerung: Ein Rückblick auf zwei Dekaden. Sucht. 2016. 62. 283-94.
- Kuczkowski K.M. The effects of drug abuse on pregnancy. Cur. Opinion Ob. Gyn. 2007. 19. 578-585.
- Minnes S. et al. Psychosocial and behavioral factors related to the post-partum placements of infants born to cocaine-using women. Child Ab. Negl. 2008. 32. 353-366.
- National Drug Intelligence Center. U.S. Department of Justice. National drug threat assessment. Washington, DC, 2014.
- Pergolizzi J.V.J., LeQuang J.A.T., Raffa R.B., Group N.R. Going beyond prescription pain relievers to understand the opioid epidemic: the role of illicit fentanyl, new psychoactive substances, and street heroin. Postgrad. Med. 2018. 130. 1-8.
- Prakash N., Wurst W. Development of dopaminergic neurons in the mammalian brain. C.M.L.S. 2006. 63. 187-206.
- Roth G.A., Abate D., Abate K.H. et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018. 392. 1736-1788.
- Seitz N.-N., Lochbühler K., Atzendorf J. et al. Trends in substance use and related disorders: analysis of the Epidemiological Survey of Substance Abuse 1995 to 2018. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2019. 116. 585-591.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Results from the 2013 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of national findings. Rockville, MD, 2014.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The NSDUH report: Substance use among women during pregnancy and following childbirth. Rockville, MD, 2009.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion & Office on Smoking and Health. The health consequences of smoking — 50 years of progress: A report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA, 2014.
- U.S. Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Administration: National drug threat assessment summary. 2016. www.dea.gov/documents/2016/11/01/2016-national-drug-threat-assessment.

/7/47.jpg)
/7/51.jpg)
/7/49.jpg)
/7/50.jpg)