Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 57, №2, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Оцінка ефективності застосування комплексу адеметіоніну, L-глутатіону, N-ацетилцистеїну (Ліводінол) при токсичному ураженні печінки (експериментальне дослідження)
Авторы: Степанов Ю.М., Діденко В.І., Кленіна І.А., Галінський О.О., Гайдар Ю.А., Петішко О.П.
ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
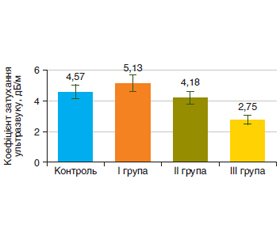
Мета дослідження — оцінка ефективності комплексу адеметіоніну, L-глутатіону, N-ацетилцистеїну (Ліводінол) на моделі індукованого тетрахлорметаном (CCl4) ураження печінки. Матеріали та методи. Для виконання дослідження було відібрано 40 лабораторних щурів. І групу становили 11 щурів, яким виконано моделювання CCl4-індукованого ураження печінки; ІI групу — 11 щурів, які після моделювання перебували 30 діб на стандартному раціоні віварію з відміною токсичного впливу; ІІІ групу — 11 щурів, які після моделювання додатково до стандартного раціону отримували 30 діб комплекс адеметіоніну, L-глутатіону, N-ацетилцистеїну (Ліводінол). Контрольна група (n = 7) складалася зі здорових щурів до початку експерименту. Після закінчення досліджень щурів після евтаназії розтинали і проводили оцінку мікроскопічної будови печінки за даними гістологічного дослідження біоптатів. Наявність процесів фіброзу оцінювали за вмістом у гомогенаті печінки неінвазивних маркерів — гідроксипроліну вільного (ГПв), гідроксипроліну білковозв’язаного (ГПб/зв) і глікозаміногліканів (ГАГ) із використанням наборів реактивів Cormаy (Польша). Хроматографічне дослідження вільних жирних кислот (ВЖК) у гомогенаті печінки було проведено з використанням апаратно-програмного комплексу на базі газового хроматографа. Ідентифікацію фракцій ВЖК проводили згідно зі стандартом метильованих жирних кислот фірми Restek (США). Вимірювання жорсткості паренхіми печінки (зсувнохвильова еластографія) і коефіцієнта затухання ультразвуку (стеатометрія) виконували за допомогою ультразвукового апарата Soneus P7 (Харків, Україна). Результати. Токсичне ураження печінки тетрахлорметаном протягом 7 тижнів викликало в щурів ураження паренхіми перипортальної зони всіх портальних трактів, вузлову трансформацію паренхіми з формуванням хибних часточок, які були розділені між собою фіброзними тяжами. Також встановлено вірогідне збільшення порівняно з контрольною групою коефіцієнта відношення ГПб/зв до ГПв — у 2,4 раза (р < 0,05), рівня ГАГ — у 1,5 раза (р < 0,05), вмісту ВЖК — у 6,9 раза (р < 0,01), жорсткості паренхіми печінки — на 30 % (р < 0,05) і коефіцієнта затухання ультразвуку — на 12 %. Після корекції токсичного ураження печінки комплексом адеметіоніну, L-глутатіону, N-ацетилцистеїну (Ліводінол) у щурів спостерігалися позитивні зміни біохімічних показників у гомогенаті печінки: зниження спектра ВЖК у 3 рази (р < 0,01) і рівня ГАГ — у 2,6 раза (р < 0,05), коефіцієнта відношення ГПб/зв до ГПв — у 3,3 раза (р < 0,05). Також у щурів 30-добове застосування гепатопротекторного комплексу Ліводінол призводило до зменшення морфологічних ознак перигепатоцелюлярного й пресинусоїдного фіброзу, зниження жорсткості паренхіми печінки — на 13 % і коефіцієнта затухання ультразвуку — на 46 %. Висновки. Включення комплексу адеметіоніну, L-глутатіону, N-ацетилцистеїну (Ліводінол) на фоні 30-добової відміни токсину порівняно з групою токсичного ураження печінки призводило до зменшення морфологічних ознак фіброзу й стеатозу печінки, зниження рівня маркерів фіброзу і вмісту вільних жирних кислот у гомогенаті печінки, а також поліпшення показників зсувнохвильової еластографії та стеатометрії.
Background. The purpose of the study is to evaluate the effectiveness of a combination of ademetionine, L-glutathione, N-acetylcysteine (Livodinol) on the tetrachloromethane (CCl4)-induced liver injury model. Materials and methods. Forty laboratory rats were selected for the study. The first group consisted of 11 rats who underwent simulation of CCl4-induced liver damage; group II included 11 rats which after the simulation were on a standard vivarium diet for 30 days without toxic effects; group III consisted of 11 rats who after modeling received a combination of ademetionine, L-glutathione, N-acetylcysteine (Livodinol) for 30 days in addition to the standard diet. The control group (n = 7) consisted of healthy rats before the start of the experiment. At the end of the studies, the rats were dissected after euthanasia and the microscopic structure of the liver was evaluated based on the histological examination of the biopsies. The presence of fibrosis was assessed by the content of non-invasive markers in the liver homogenate — free hydroxyproline (HPf), protein-bound hydroxyproline (HPp/b) and glycosaminoglycans (GAG) using Cormay reagent kits (Poland). The chromatographic study of free fatty acids (FFA) in the liver homogenate was carried out using the hardware and software complex based on gas chromatograph. The identification of FFA fractions was carried out according to the fatty acid methyl esters standard by Restek company (USA). Liver parenchyma stiffness (shear wave elastography) and controlled attenuation parameter (steatometry) were measured using a Soneus P7 ultrasound machine (Kharkiv, Ukraine). Results. Toxic damage to the liver with tetrachloromethane for 7 weeks caused damage to the parenchyma of the periportal zone of all portal tracts, nodular transformation of the parenchyma with the formation of pseudolobules, which were separated from each other by fibrous strands. There was also a significant increase in the HPp/b to HPf ratio, by 2.4 times (p < 0.05) compared to the control group, in the GAG level by 1.5 times (p < 0.05), in the FFA content by 6.9 times (p < 0.01), in the stiffness of the liver parenchyma by 30 % (p < 0.05) and the controlled attenuation parameter by 12 %. After the correction of toxic damage to the liver with a combination of ademetionine, L-glutathione, N-acetylcysteine (Livodinol), rats had positive changes in biochemical indicators of the liver homogenate: a 3-fold (p < 0.01) decrease in the FFA and a 2.6-fold (p < 0.05) in the GAG level, in the HPp/b to HPf ratio — by 3.3 times (р < 0.05. Also, 30-day use of the hepatoprotective combination Livodinol in rats led to a reduction in the morphological signs of perihepatocellular and presinusoidal fibrosis, a decrease in the stiffness of the liver parenchyma by 13 %, and the controlled attenuation parameter by 46 %. Conclusions. The inclusion of a combination of ademetionine, L-glutathione, N-acetylcysteine (Livodinol) against the background of 30-day withdrawal of the toxin compared to the group of toxic liver damage led to a decrease in the morphological signs of fibrosis and steatosis of the liver, a reduction in the level of fibrosis markers and the content of free fatty acids in the liver homogenate, as well as an improvement of the shear wave elastography and steatometry indicators.
токсичне ураження печінки; експериментальне дослідження; застосування; комплекс адеметіоніну, L-глутатіону, N-ацетилцистеїну (Ліводінол)
toxic liver damage; experimental research; treatment; combination of ademetionine, L-glutathione, N-acetylcysteine (Livodinol)
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Висновки
- Younossi Z.M. et al. Epidemiology of chronic liver diseases in the USA in the past three decades. Gut. 2020. Vol. 69(3). P. 564-568.
- Paik J.M. et al. Changes in the Global Burden of Chronic Liver Diseases From 2012 to 2017: The Growing Impact of NAFLD. Hepato–logy (Baltimore, Md.). 2020. Vol. 72(5). P. 1605-1616.
- Torbenson M., Washington K. Pathology of liver disease: advances in the last 50 years. Hum. Pathol. 2020. № 95. P. 78-98.
- Thapa K. et al. Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic Liver Diseases: Promising Molecular Drug Targets and their Clinical Development. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2021. Vol. 18(3). P. 333-353.
- Buratti S., Lavine J.E. Drugs and the liver: advances in meta–bolism, toxicity, and therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2002. Vol. 14(5). P. 601-607.
- Ray G. Management of liver diseases: Current perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022. Vol. 28(40). P. 5818-5826.
- Song D.S. Medical Treatment of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2020. Vol. 76(2). P. 65-70.
- Lv H. et al. Unraveling the Potential Role of Glutathione in Multiple Forms of Cell Death in Cancer Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019. Vol. 2019. P. 3150145.
- Vázquez-Meza H. et al. Cellular Compartmentalization, Glutathione Transport and Its Relevance in Some Pathologies. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. Vol. 12(4). P. 834.
- Tardiolo G., Bramanti P., Mazzon E. Overview on the Effects of N-Acetylcysteine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules. 2018. Vol. 23(12). P. 3305.
- Atalay F. et al. N-Acetyl Cysteine Has Both Gastro-Protective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Experimental Rat Models: Its Gastro-Protective Effect Is Related to Its In Vivo and In Vitro Antioxidant Properties. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016. Vol. 117(2). P. 308-319.
- Raikhelson K.L., Kondrashina E.A. Аdеmethionine in the treatment of fatigue in liver diseases: a systematic review. Ter. Arkh. 2019. Vol. 91(2). P. 134-142.
- Guo T., Chang L., Xiao Y., Liu Q. S-adenosyl-L-methionine for the treatment of chronic liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015. Vol. 10(3). P. e0122124.
- Степанов Ю.М. та ін. Особливості впливу комплексу Ліводінол® у пацієнтів з неалкогольною жировою хворобою печінки (власне дослідження). Український медичний часопис. 2022. № 5(151). С. 2-7.

/1.jpg)
/2.jpg)
/3.jpg)
/4.jpg)