Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 19, №2, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Зміни ендотеліальної функції та оксидантного статусу при інсулінорезистентності й ожирінні за умов йодного дефіциту
Авторы: T.V. Todoriv, N.M. Voronych-Semchenko, O.M. Didushko
Ivano-Frankivsk National Medical University, Ivano-Frankivsk, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
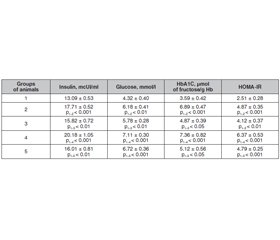
Актуальність. Актуальність теми зумовлена значною поширеністю серцево-судинних захворювань та підвищенням витрат на медичне обслуговування, високим ризиком інвалідності, що характеризує медико-соціальну складову проблеми. Патологічні зміни можуть бути не тільки проявом кардіоваскулярної системи, а й розвиватися внаслідок інших захворювань, зокрема цукрового діабету, ожиріння та тиреоїдної патології. Одним із головних механізмів інвалідизації та смертності є макросудинні ускладнення, що можуть виникати за умов ендотеліальної дисфункції та оксидативного стресу. Мета дослідження: вивчити особливості змін показників ендотеліальної системи та оксидантного статусу у тварин із інсулінорезистентністю й ожирінням при належному забезпеченні йодом та йодному дефіциті. Матеріали та методи. Дослідження проведені на 75 статевозpілих щурах, які отримували високовуглеводну, високожирову дієти за умов належного та обмеженого забезпечення йодом, із подальшим аналізом маркерів вуглеводного обміну, тиреоїдного статусу, показників ендотеліальної функції, перекисного окиснення ліпідів й антиоксидантного захисту. Результати. Розвиток інсулінорезистентності та ожиріння при навантаженні дієти фруктозою та жирами супроводжується розвитком ендотеліальної дисфункції: у сироватці крові збільшується рівень ендотеліну-1 та активується індуцибельна NO-синтаза (iNO-синтаза), у міокарді зростає активність iNO-синтази порівняно з даними тварин, у яких харчовий раціон стандартний. Розвиток оксидативного стресу в дослідних тварин характеризує зростання вмісту дієнових кон’югат і реактивних сполук тіобарбітурової кислоти в сироватці крові та міокарді на тлі пригнічення антиоксидантних ферментів сироватки крові (каталаза, супероксиддисмутаза, церулоплазмін, глутатіонпероксидаза, глутатіонредуктаза). Ступінь ендотеліальної дисфункції та інтенсивність ліпопероксидації зростають при гіпотиреоїдній дисфункції на тлі йодного дефіциту. Висновки. Метаболічні порушення за умов інсулінорезистентності й ожиріння характеризуються розвитком ендотеліальної дисфункції та оксидативного стресу, що є предикторами виникнення кардіоваскулярних ризиків. Їх інтенсивність залежить від вуглеводного та тиреоїдного гомеостазу.
Background. The topicality of the theme is due to the significant prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and an increase in costs for medical care, the high risk of disability, which characterizes the medical and social component of the problem. Pathological changes can be a manifestation not only of a cardiovascular disorder, but also develop as a result of other diseases, including diabetes mellitus, obesity, and thyroid pathology. One of the main mechanisms of morbidity and mortality is macrovascular complications that can occur in endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress. The purpose of the research is to study the peculiarities of changes in the parameters of the endothelial system and oxidant status in animals with insulin resistance and obesity under conditions of adequate iodine supply and iodine deficiency. Materials and methods. Study included 75 sexually mature rats having received a high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet under conditions of adequate and limited iodine supply, followed by analysis of markers of carbohydrate metabolism, thyroid status, indices of endothelial function, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant protection. Results. The development of insulin resistance and obesity in a diet loaded with fructose and fats is accompanied by the development of endothelial dysfunction: in the blood serum, the level of endothelin-1 increases and inducible NO-synthase (iNO-synthase) is activated, in the myocardium, the activity of iNO-synthase increases compared to the data in animals who received a standard diet. The development of oxidative stress in experimental animals characterizes an increase in the content of diene conjugates and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances in blood serum and myocardium against the background of inhibition of serum antioxidant enzymes (catalase, superoxide dismutase, ceruloplasmin, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase). The degree of endothelial dysfunction and the intensity of lipoperoxidation increase with hypothyroid dysfunction against the background of iodine deficiency. Conclusions. Metabolic disorders under the conditions of insulin resistance and obesity are characterized by the development of endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress, which are the predictors of the development of cardiovascular risks. Their intensity depends on carbohydrate and thyroid homeostasis.
серцево-судинна система; інсулінорезистентність; ожиріння; тиреоїдний гомеостаз; ендотеліальна дисфункція; про-/антиоксидантна система
cardiovascular system; insulin resistance; obesity; thyroid homeostasis; endothelial dysfunction; pro-/antioxidant system
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Kobrynska O.Ya., Didushko O.M. Current possibilities of influencing the main cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2022. 18(8). 426-31. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.18.8.2022.1220.
- Vardas P.E., Asselbergs F.W., van Smeden M., Friedman P. The year in cardiovascular medicine 2021: digital health and innovation. Eur. Heart J. 2022. 43(4). 271-9. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab874.
- Aksenov E.V. Endothelial Dysfunction and Ways of its Prevention during Percutaneous Coronary Interventions by Recanalization of Coronary Arteries. Ukrainian Journal of Medicine, Biology and Sport. 2019. 4(5). 102-8. doi: 10.26693/jmbs04.05.102 (in Ukrainian).
- Sirenko Yu.M. The state of the problem of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in Ukraine. Medicine of Ukraine. 2022. 2(258). 11-4. doi: 10.37987/1997-9894.2022.2(258).264084 (in Ukrainian).
- Cosentino F., Bhatt D.L., Marx N., Verma S. The year in cardiovascular medicine 2021: diabetes and metabolic disorders. Eur. Heart J. 2022. 43(4). 263-70. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab876.
- Pankiv V.I., Yuzvenko T.Yu., Pankiv I.V. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and subclinical hypothyroidism: focusing on the role of cholecalciferol. Problems of Endocrine Pathology. 2019. 2. 46-51. doi: 10.21856/j-PEP.2019.2.07.
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C. et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022 Jan. 183. 109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119.
- Eades C.E., France E.F., Evans J.M. Prevalence of impaired glucose regulation in Europe: a meta-analysis. Eur. J. Public Health. 2016 Aug. 26(4). 699-706. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckw085.
- Lin X., Li H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 6. 12. 706978. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.706978.
- Chooi Y.C., Ding C., Magkos F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism. 2019 Mar. 92. 6-10. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.09.005.
- Dinets A.V., Gorobeiko M.B., Zdorna V.V., Hoperia V.H., Lovin A.V. An integrated approach for obesity management: the effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide 1 agonist and life-style interventions for obesity management. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2022. 18(3). 12-9. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.18.3.2022.1161 (in Ukrainian).
- Di Daniele N., Tesauro M., Mascali A., Rovella V., Scuteri A. Lower Heart Rate Variability Is Associated with Lower Pulse Pressure Amplification: Role of Obesity. Pulse (Basel). 2018. 5(1–4). 99-105. doi: 10.1159/000479701.
- Kamyshna І.І., Pavlovych L.B., Maslyanko V.A., Chornenka Zh.A. Epidemiological assessment of dynamics of the prevalence and incidence of the thyroid gland diseases in Ukraine and Chernivtsi region. Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2021. 20(3). 75-81. doi: 10.24061/1727-4338.XX.3.77.2021.11.
- Liu R., Li L., Shao C., Cai H., Wang Z. The Impact of Diabetes on Vascular Disease: Progress from the Perspective of Epidemics and Treatments. J. Diabetes Res. 2022. 2022. 1531289. doi: 10.1155/2022/1531289.
- Turchina S.I., Shushlyapina E.V., Kosovtsova A.V., Shlya–khova N.V. Thyroid Dysfunction and Childhood Obesity (literature review and own research). Modern Pediatrics. Ukraine. 2020. 2(106). 56-62. doi: 10.15574/SP.2020.106.56.
- Gallo G., Volpe M., Savoia C. Endothelial Dysfunction in Hypertension: Current Concepts and Clinical Implications. Front. Med. (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 20. 8. 798958. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.798958.
- Poredos P., Poredos A.V., Gregoric I. Endothelial Dysfunction and Its Clinical Implications. Angiology. 2021 Aug. 72(7). 604-615. doi: 10.1177/0003319720987752.
- Kröller-Schön S., Daiber A., Steven S., Oelze M., Frenis K., Kalinovic S. et al. Crucial role for Nox2 and sleep deprivation in aircraft noise-induced vascular and cerebral oxidative stress, inflammation, and gene regulation. Eur. Heart J. 2018. 39(38). 3528-39. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy333.
- Todoriv T.V., Bagrii M.M., Voronych-Semchenko N.M. State of endothelial function, lipid spectrum and features of coronary vessels structure of rats with obesity and insulin resistance under iodine deficiency conditions. Fiziolohichnyi zhurnal. 2021. 67(6). 21-31. doi: 10.15407/fz67.06.021.
- Malevych N.M., Yaroshenko T.Ya. Impact of acute hypoxic hypoxia on the oxidative and non-oxidative phases of l-arginine metabolism in myocardium and aorta of rats in age aspect. Medical and Clinical Chemistry. 2021. 23(2). 41-47. doi: 10.11603/mcch.2410-681X.2021.i2.12237.
- Maguire J.J., Davenport A.P. Endothelin receptors and their antagonists. Semin. Nephrol. 2015 Mar. 35(2). 125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2015.02.002.
- Asanov E.O., Gavalko A.V., Duzhak G.V., Naskalova S.S., Antonyuk-Shcheglova І.А., Shatilo V.B. Microcirculation and vasomotor function of the endothelium in elderly people with impaired glucose tolerance. Fiziolohichnyi zhurnal. 2022. 68(4). 28-32. doi: 10.15407/fz68.04.028 (in Ukrainian).
- Ouerd S., Idris-Khodja N., Trindade M., Ferreira N.S., Berillo O., Coelho S.C. et al. Endothelium-restricted endothelin-1 overexpression in type 1 diabetes worsens atherosclerosis and immune cell infiltration via NOX1. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021. 117(4). 1144-53. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa168.
- Zhou S.S., Jin J.P., Wang J.Q., Zhang Z.G., Freedman J.H., Zheng Y. et al. miRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: potential biomar–kers, therapeutic targets and challenges. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018. 39(7). 1073-84. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.30.
- Danylovych Yu.V., Danylovych H.V., Kosterin S.O. Рossible importance of adenylate cyclase signaling pathway in the synthesis of nitric oxide by myometrium mitochondria. Fiziolohichnyi zhurnal. 2022. 68(4). 33-9. doi: 10.15407/fz68.04.033 (in Ukrainian).
- Bilovol O.M., Kniazkova I.I., Bohun M.V., Kuzminova N.V., Osovska N.Y. Treatment of heart failure in patients with diabetes mellitus. World of Medicine and Biology. 2020. 1(71). 18-22. doi: 10.26724/2079-8334-2020-1-71-18-22.
- Voloshchuk O.M., Kopylchuk Н.P. Intensity of free radical processes in rat skeletal muscles under the conditions of different dietary supply with nutrients. Fiziolohichnyi zhurnal. 2022. 68(4). 48-56. doi: 10.15407/fz68.04.048 (in Ukrainian).
- Sorokman T.V., Popeliuk N.O. Obesity in children: criteria for predicting the development of hypertension. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2020. 16(2). 66-72. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.16.2.2020.201299 (in Ukrainian).