Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №1, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Роль мікроРНК у розвитку захворювань гепатобіліарної системи
Авторы: Абатуров О.Є., Бабич В.Л.
Дніпровський державний медичний університет, м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
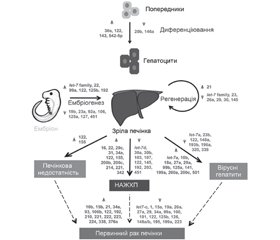
У науковому огляді висвітлено роль мікроРНК у розвитку захворювань гепатобіліарної системи. Для написання статті здійснювався пошук інформації з використанням баз даних Scopus, Web of Science, MedLine, PubMed, Google Scholar, EMBASE, Global Health, The Cochrane Library. Авторами надана інформація щодо генерації різними типами клітин гепатобіліарної системи певного спектра мікроРНК. Автори наводять, що гепатоцит-асоційованими мікроРНК є miR-122-5p, miR-101, miR-192, miR-193, miR-194, miR-802. Відомо, що в регуляції запального процесу беруть участь численні мікроРНК: miR-21, miR-29а, miR-96, miR-122, miR-125b, miR-132, miR-155, miR-146a, miR-150, miR-155, miR-181 і let-7. З безлічі мікроРНК, що беруть участь у регуляції процесу запалення в печінці, найбільш вивченими є miR-122, miR-155. Показано, що мікроРНК — let-7d, miR-15b, miR-19b, miR-21, miR-24, miR-29c, miR-122, miR-145, miR-155, miR-199, miR-200c, miR-378a — є найважливішими модуляторами активності розвитку фіброзу в різних тканинах організму, у тому числі в тканині печінки. Наведено мікроРНК, які беруть участь у розвитку TGF-β1-індукованого фіброзу печінки. Науковці вважають, що оскільки мікроРНК регулюють клітинний цикл, проліферацію і апоптоз клітин, вони є факторами, які суттєво визначають розвиток пухлин гепатобіліарної системи. Підкреслено, що зміни мікроРНК-профілю в тканині печінки або сироватці крові мають свою діагностичну цінність. Наведені модуляції мікроРНК, що з великим ступенем імовірності асоційовані з конкретними хворобами печінки й жовчовивідних шляхів. Отже, у розвитку захворювань гепатобіліарної системи важливу роль відіграють різні мікроРНК. Певний спектр мікроРНК генерується різними типами клітин і відіграє важливу роль у дозріванні й функціонуванні гепатобіліарної системи. МікроРНК опосередковано беруть участь у синтезі білків, диференціюванні клітин, тканин і відіграють важливу патогенетичну роль у розвитку захворювань гепатобіліарної системи. Найважливішою властивістю мікроРНК є їх висока стійкість до дії ферментативних субстанцій, що дозволяє використовувати їх як діагностичні або прогностичні біомаркери.
The role of miRNA in the development of hepatobiliary diseases is considered in the scientific review. To write the article, information was searched using Scopus, Web of Science, MedLine, PubMed, Google Scholar, EMBASE, Global Health, The Cochrane Library databases. The authors provided information on the generation of a certain spectrum of miRNA by different types of cells of the hepatobiliary system. The authors state that miR-122-5p, miR-101, miR-192, miR-193, miR-194, miR-802 are hepatocyte-associated microRNAs. It is known that numerous microRNAs are involved in the regulation of the inflammatory process: miR-21, miR-29a, miR-96, miR-122, miR-125b, miR-132, miR-155, miR-146a, miR-150, miR-155, miR-181 and let-7. Among the many microRNAs involved in the regulation of inflammation in the liver, miR-122 and miR-155 are the most studied. It is stated that microRNAs such as let-7d, miR-15b, miR-19b, miR-21, miR-24, miR-29c, miR-122, miR-145, miR-155, miR-199, miR-200c, miR-378a are the most important modulators for the activity of fibrosis development in various tissues of the body, including liver tissue. MicroRNAs involved in the development of TGF-β1-induced liver fibrosis are presented. Scientists believe that since microRNAs regulate the cell cycle, proliferation and apoptosis of cells, they are factors that significantly affect the development of hepatobiliary tumors. It is emphasized that changes in miRNA profile in liver tissue or blood serum have their diagnostic value. Modulations of microRNAs are shown, which are associated with specific diseases of the liver and biliary tract with a high degree of probability. Thus, various miRNAs play an important role in the development of hepatobiliary diseases. A certain spectrum of miRNAs is generated by different cell types and plays an important role in the maturation and functioning of the hepatobiliary system. MicroRNAs indirectly participate in the synthesis of proteins, differentiation of cells, tissues and play an important pathogenetic role in the development of hepatobiliary diseases. The most important feature of microRNAs is their high resistance to the action of enzymatic substances, which allows them to be used as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers.
мікроРНК; гепатобіліарна система; запалення; фіброз; діагностичні маркери; огляд
microRNA; miRNA; miR; hepatobiliary system; inflammation; fibrosis; diagnostic markers; review
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Абатуров О.Є., Бабич В.Л. Роль мікро-РНК при захворюваннях біліарної системи. Здоров’я дитини. 2017. 7(12). 155-161. DOI: 10.22141/2224-0551.12.7.2017.116191
- Абатуров О.Є., Бабич В.Л. Світ мікроРНК гепатобіліарної системи. Здоров’я дитини. 2021. 1(16). 122-131. DOI: 10.22141/2224-0551.16.1.2021.226462
- Вахрушев Я.М., Хохлачева Н.А., Михеева П.С., Сучкова Е.В. Механизмы нарушений моторно-эвакуаторной функции желчного пузыря и их значение в развитии холелитиаза. Архивъ внутренней медицины. 2018 . 1. 53-58.
- Волосовець О.П., Зубаренко О.В., Кривопустов С.П. та ін. Педіатрія (гастроентерологія та патологія раннього віку): навч. посібник. Одеса: Друк Південь, 2017. 264 с.
- Пархоменко Л.К., Страшок Л.А., Ісакова М.Ю., Єщенко А.В., Хоменко М.А., Павлова О.С., Кварацхелія Т.М. Удосконалення діагностики й лікування гепатобіліарної патології в підлітків з ожирінням. Здоров’я дитини. 2018. 14 (Додаток 1. Дитяча гастроентерологія та нутриціологія). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.22141/2224-0551.13.0.2018.131180.
- Шадрін О.Г., Чернега Н.Ф. Мікробіота та захворювання гепатобіліарної системи: нові можливості в лікуванні дітей раннього віку. Здоров’я дитини. 2015. 65(5). 23-29.
- Akbulut U.E. Plasma MicroRNA (miRNA)s as Novel Markers of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Biomarkers in Nutrition. 2022. 517-534. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-07389-2_30.
- Bala S., Szabo G. MicroRNA Signature in Alcoholic Liver Di–sease. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012. 2012. 498232. doi: 10.1155/2012/498232.
- Bandiera S., Pfeffer S., Baumert T.F., Zeisel M.B. miR-122 — a key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015 Feb. 62(2). 448-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.004.
- Barbato A., Piscopo F., Salati M., Reggiani-Bonetti L., Franco B., Carotenuto P. Micro-RNA in Cholangiocarcinoma: Implications for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy. Journal of Molecular Pathology. 2022. 3(2). 88-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3020009.
- Blaya D., Aguilar-Bravo B., Hao F. Expression of microRNA-155 in inflammatory cells modulates liver injury. Hepatology. 2018 Feb 8. doi: 10.1002/hep.29833.
- Bouwens L., De Bleser P., Vanderkerken K. et al. Liver cell he–terogeneity: functions of non-parenchymal cells. Enzyme. 1992. 46(1-3). 155-68. PMID: 1289080.
- Calvopina D.A., Coleman M.A., Lewindon P.J., Ramm G.A. Function and Regulation of MicroRNAs and Their Potential as Biomar–kers in Paediatric Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016 Oct 27. 17(11). pii: E1795. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111795.
- Chen C., Jiang J., Fang M. et al. MicroRNA-129-2-3p directly targets Wip1 to suppress the proliferation and invasion of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Cancer. 2020. 11(11). 3216-24. doi:10.7150/jca.41492.
- Chen Y., Verfaillie C.M. MicroRNAs: the fine modulators of liver development and function. Liver Int. 2014 Aug. 34(7). 976-90. doi: 10.1111/liv.12496.
- Demarez C., Hubert C., Sempoux C., Lemaigre F.P. Expression of Molecular Differentiation Markers Does Not Correlate with Histological Differentiation Grade in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2016. 11(6). e0157140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157140.
- Finch M.L., Marquardt J.U., Yeoh G.C., Callus B.A. Regulation of microRNAs and their role in liver development, regeneration and di–sease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2014 Sep. 54. 288-303. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.04.002.
- Friedman S.L. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010 Aug. 7(8). 425-36. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.97.
- Goldschmidt I., Thum T., Baumann U. Circulating miR-21 and miR-29a as Markers of Disease Severity and Etiology in Cholestatic Pediatric Liver Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2016 Mar. 5(3). 28. doi: 10.3390/jcm5030028.
- Guo X., Lv X., Ma Y., Chen L., Chen Y. Circulating miR-21 serves as a serum biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma and correlated with distant metastasis. Oncotarget. 2017. 8. 44050-8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17211.
- Hall C., Sato K., Wu N. et al. Regulators of Cholangiocyte Proliferation. Gene Expr. 2017 Feb 10. 17(2). 155-171. doi: 10.3727/105221616X692568.
- Hayes C.N., Chayama K. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016 Feb 24. 17(3). 280. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030280.
- Hegazy M.A., Abd ALgwad I., Abuel Fadl S., Sayed Hassan M., Ahmed Rashed L., Hussein M.A. Serum Micro-RNA-122 Level as a Simple Noninvasive Marker of MAFLD Severity. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 May 19. 14. 2247-2254. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S291595. PMID: 34040409; PMCID: PMC8142686.
- Hsu S.H., Wang B., Kota J. et al. Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver. J. Clin. Invest. 2012 Aug. 122(8). 2871-83. doi: 10.1172/JCI63539.
- Hu J., Xu Y., Hao J. et al. MiR-122 in hepatic function and liver diseases. Protein Cell. 2012 May. 3(5). 364-71. doi: 10.1007/s13238-012-2036-3.
- Huang Y.H., Yang Y.L., Wang F.S. The Role of miR-29a in the Regulation, Function, and Signaling of Liver Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018 Jun 27. 19(7). pii: E1889. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071889.
- Human miRNA Disease Database. http://cmbi.bjmu.edu.cn/hmdd.
- Jiang X.P., Ai W.B., Wan L.Y. et al. The roles of microRNA families in hepatic fibrosis. Cell. Biosci. 2017 Jul 4. 7. 34. doi: 10.1186/s13578-017-0161-7.
- Kennedy I., Francis H., Meng F. et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic potentials of microRNAs in cholangiopathies. Liver Res. 2017 Jun. 1(1). 34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.03.003.
- Kerr T.A., Korenblat K.M., Davidson N.M. MicroRNAs and liver disease. Transl. Res. 2011. 157. 241-52. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2 011.01.008.
- Kitano M., Bloomston P.M. Hepatic stellate cells and microRNAs in pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2016. 5. E38. doi: 10.3390/jcm5030038.
- Krützfeldt J., Rajewsky N., Braich R. et al. Silencing of –microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature. 2005 Dec 1. 438(7068). 685-9. doi: 10.1038/nature04303.
- Kul K., Serin E., Yakar T. et al. Autonomic neuropathy and gallbladder motility in patients with liver cirrhosis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2015 May. 26(3). 254-8. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2015.4469.
- Lekka E., Hall J. Non-coding RNAs in Disease. FEBS Lett. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13182.
- Letelier P., Riquelme I., Hernández A.H., Guzmán N., Farías J.G., Roa J.C. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Biliary Tract Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016 May. 17(5). 791. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050791.
- Li J., Gong J., Li P. et al. Knockdown of microRNA-155 in Kupffer cells results in immunosuppressive effects and prolongs survival of mouse liver allografts. Transplantation. 2014 Mar 27. 97(6). 626-35. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000061.
- Li M., Tang Y., Wu L. et al. The hepatocyte-specific HNF4α/miR-122 pathway contributes to iron overload-mediated hepatic inflammation. Blood. 2017 Aug 24. 130(8). 1041-1051. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-12-755967.
- Li S.C., Wang F.S., Yang Y.L., Tiao M.M., Chuang J.H., Huang Y.H. Microarray Study of Pathway Analysis Expression Profile Associated with MicroRNA-29a with Regard to Murine Cholestatic Liver Injuries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016 Mar 1. 17(3). 324. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030324.
- Liu J., Xiao Y., Wu X.K., Jiang L.C., Yang S.R., Ding Z.M. et al. A circulating microRNA signature as noninvasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. BMC Genomics. 2018. 19. 188. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4575-3
- Loosen S.H., Schueller F., Trautwein C. et al. Role of circulating microRNAs in liver diseases. World J. Hepatol. 2017 Apr 28. 9(12). 586-594. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i12.586.
- López-Riera M., Conde I., Castell J.V., Jover R. A Novel MicroRNA Signature for Cholestatic Drugs in Human Hepatocytes and Its Translation into Novel Circulating Biomarkers for Drug-Induced Liver Injury Patients. Toxicological Sciences. 2020. 2(173). 229-43. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfz138.
- Lu H., Lei X., Liu J. et al. Regulation of hepatic microRNA expression by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha. World J. Hepatol. 2017 Feb 8. 9(4). 191-208. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i4.191.
- Malarkey D.E., Johnson K., Ryan L. et al. New insights into functional aspects of liver morphology. Toxicol. Pathol. 2005. 33(1). 27-34. doi: 10.1080/01926230590881826.
- Meng Z., Fu X., Chen X. et al. miR-194 is a marker of hepatic epithelial cells and suppresses metastasis of liver cancer cells in mice. Hepatology. 2010 Dec. 52(6). 2148-57. doi: 10.1002/hep.23915.
- Momen-Heravi F., Bala S. miRNA regulation of innate immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018 Apr 14. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MIR1117-459R.
- Murakami Y., Toyoda H., Tanaka M. et al. The progression of liver fibrosis is related with overexpression of the miR-199 and 200 families. PLoS One. 2011 Jan 24. 6(1). e16081. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016081.
- Nejad C., Pillman K.A., Siddle K.J. et al. miR-222 isoforms are differentially regulated by type-I interferon. RNA. 2018 Mar. 24(3). 332-341. doi: 10.1261/rna.064550.117.
- Neudecker V., Yuan X., Bowser J.L., Eltzschig H.K. MicroRNAs in mucosal inflammation. J. Mol. Med. (Berl). 2017 Sep. 95(9). 935-949. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1568-7.
- Oda S., Takeuchi M., Akai S. et al. miRNA in Rat Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells and Hepatocytes and Application to Circulating Biomarkers that Discern Pathogenesis of Liver Injuries. Am. J. Pathol. 2018 Apr. 188(4). 916-928. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.12.007.
- Otsuka M., Kishikawa T., Yoshikawa T. et al. MicroRNAs and liver disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2017 Jan. 62(1). 75-80. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.53.
- Rangel G., Wanram S., Umemura T. Circulating Exosomal –microRNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers in Cholangicarcinoma: A Systematic Review. Nanomedicine and Nanoscience Technology: Open Access. 2021. 1(1). 1-4.
- Sakamoto T., Morishita A., Nomura T., Tani J., Miyoshi H. et al. Identification of microRNA profiles associated with refractory primary biliary cirrhosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016 Oct. 14(4). 3350-6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5606.
- Statistics about the current Human GENCODE Release (version 27) (January 2017 freeze, GRCh38) — Ensembl 90. https://www.gencodegenes.org/stats/current.html.
- Szabo G., Bala S. MicroRNAs in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013 Sep. 10(9). 542-52. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.87.
- Tang Y., Jia W., Niu X. et al. CCL2 is Upregulated by Decreased miR-122 Expression in Iron-Overload-Induced Hepatic Inflammation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017. 44(3). 870-883. doi: 10.1159/000485355.
- Thakral S., Ghoshal K. miR-122 is a unique molecule with great potential in diagnosis, prognosis of liver disease, and therapy both as –miRNA mimic and antimir. Curr. Gene Ther. 2015. 15(2). 142-50. doi: 10.2174/1566523214666141224095610. PMID: 25537773.
- Tsai W.C., Hsu S.D., Hsu C.S. et al. MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2012 Aug. 122(8). 2884-97. doi: 10.1172/JCI63455.
- Tu X., Zhang H., Zhang J. et al. MicroRNA-101 suppresses liver fibrosis by targeting the TGFβ signalling pathway. J. Pathol. 2014 Sep. 234(1). 46-59. doi: 10.1002/path.4373.
- Wang W., Bian H., Li F. et al. HBeAg induces the expression of macrophage miR-155 to accelerate liver injury via promoting production of inflammatory cytokines. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018 Jul. 75(14). 2627-2641. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2753-8.
- Wang X.W., Heegaard N.H., Orum H. MicroRNAs in liver di–sease. Gastroenterology. 2012 Jun. 142(7). 1431-43. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.007.
- Watanabe K., Ohnishi S., Manabe I. et al. KLF6 in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: role of fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis. Gastroentero–logy. 2008 Jul. 135(1). 309-12. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.06.014.
- Yamaura Yu., Naoyuki T., Shingo T., Shinsaku T. at al. Serum microRNA profiles in patients with chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or drug-induced liver injury. Clinical Biochemistry. 2017. 18(50). 1034-39. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.08.010.
- Yang C., Zheng S.D., Wu H.J., Chen S.J. Regulatory Mechanisms of the Molecular Pathways in Fibrosis Induced by MicroRNAs. Chin. Med. J. (Engl). 2016 Oct 5. 129(19). 2365-72. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.190677.
- Yeligar S., Tsukamoto H., Kalra V.K. Ethanol-induced expression of ET-1 and ET-BR in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and human endothelial cells involves hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and –microrNA-199 J. Immunol. 2009 Oct 15. 183(8). 5232-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901084.
- Yin X., Chai Z., Sun X., Chen J., Wu X., Yang L., Zhou X., Liu F. Overexpression of microRNA‑96 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma cells via MTSS1. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2020. 4(19). 2757-65. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8502.
- Yu F., Jiang Z., Chen B. et al. NEAT1 accelerates the progression of liver fibrosis via regulation of microRNA-122 and Kruppel-like factor 6. J. Mol. Med. (Berl). 2017 Nov. 95(11). 1191-1202. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1586-5.
- Zhang T., Yang Z., Kusumanchi P., Han S., Liangpunsakul S. Critical Role of microRNA-21 in the Pathogenesis of Liver Diseases. Front. Med. 2020. 7. 7. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00007.