Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 18, №1, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Ефективність екстракту Vitex agnus castus у лікуванні первинної дисменореї
Авторы: Semenyna H.B., Korytko O.O.
Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
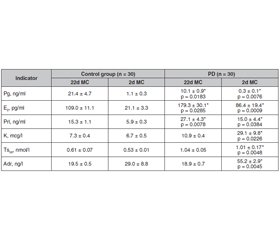
Актуальність. Первинна дисменорея (ПД) — один з найпоширеніших видів гінекологічної патології, що спостерігається у 31–52 % молодих жінок, серед яких у 10 % інтенсивність процесу призводить до інвалідності. Патогенез ПД враховує вплив представника ейкозаноїдів тромбоксану А2 з вираженою судинозвужувальною дією. У статті надані результати клініко-гормонального обстеження жінок з ПД та розроблена на цій основі методика лікування. Мета: розробити й оцінити ефективність лікування ПД з урахуванням багатокомпонентного патогенезу захворювання. Матеріали та методи. Під спостереженням перебувало 60 жінок, випадковим чином розподілених на дві групи: 30 жінок із ПД (основна група) та 30 здорових жінок (контрольна група). Діагноз ПД встановлювався на підставі скарг пацієнток на болючі менструації та супутні симптоми, за винятком органічної гінекологічної патології та захворювань внутрішніх органів, на консультаціях у гінеколога й ендокринолога. Лікування хворих на ПД проводили комбінованим препаратом, до складу якого входять стандартизований екстракт Vitex agnus castus L., індол-3-карбінол, 3,3-диіндоліл-метан, екстракт пасифлори, екстракт каліфорнійської ешольції. Результати. В результаті лікування у хворих на ПД значно зменшилася інтенсивність болю, а у 60 % біль зник повністю, у всіх зник страх очікування наступної менструації, значно зменшилися прояви вегетативно-судинної системи (з 17 до 3 % пацієнток), вегетативні (від 10 до 0 % хворих), метаболічні й ендокринні (від 13 до 0 % хворих) розлади та розлади емоційно-психічної сфери (від 23 до 7 % хворих). Через 1 місяць після лікування поліпшення якості життя відзначали 70 % (21/30) пацієнток з ПД, а підвищення працездатності — 60 % (18/30), через 2 місяці — 93 % (28/30) і 83 % (25/30) відповідно. В жодної пацієнтки під час лікування не було виявлено побічних ефектів. Висновки. З огляду на безпеку та високу терапевтичну ефективність препарат на основі екстракту Vitex agnus castus можна рекомендувати для лікування молодих хворих із ПД тривалістю не менше трьох місяців.
Background. Primary dysmenorrhea (PD) is one of the most common types of gynecological pathology and is observed in 31–52 % of young women, in 10 % of them the pain is so intense that leads to disability. In the pathogenesis of PD consider a representative of eicosanoids — thromboxane A2 with a pronounced vasoconstrictor effect. The article presents the results of clinical and hormonal examination of women with PD and developed on this basis a method of treatment. The purpose was to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment of PD, taking into account the multicomponent pathogenesis of the disease. Materials and methods. There were 60 women observation, randomly divided into two groups: 30 women with PD (main group) and 30 healthy women (control group). PD was diagnosed on the basis of patients’ complaints of painful menstruation and related symptoms, excluding organic gynecological pathology and diseases of the internal organs in consultation with a physician and endocrinologist. Treatment of patients with PD was performed with a combined drug, which includes a standardized extract of Vitex agnus castus L., indole-3-carbinol, 3,3-diindolyl-methane, passionflower extract, California escholzia extract. Results. As a result of treatment in patients with PD significantly reduced the intensity of pain, and 60 % completely disappeared pain, all disappeared fear of waiting for the next menstruation, significantly reduced the manifestations of autonomic vascular (from 17 % of patients to 3 %), autonomic (from 10 % of patients to 0 %), metabolic and endocrine (from 13 % of patients to 0 %) disorders and disorders of the emotional and mental sphere (from 23 % of patients to 7 %), no patient had a combination of symptoms. Conclusions. Given the safety, high therapeutic efficacy, the drug based on Vitex agnus castus extract can be recommended for the treatment of young patients with PD lasting at least 3 months.
менструальний біль; гормональний баланс; первинна дисменорея
menstrual pain; hormonal balance; primary dysmenorrhea
Introduction
Materials and methods
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
- Armour M., Parry K., Manohar N., Holmes K., Ferfolja T., Curry C., MacMillan F., Smith C.A. The Prevalence and Academic Impact of Dysmenorrhea in 21,573 Young Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Womens Health (Larchmt). 2019 Aug. 28(8). 1161-1171. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2018.7615.
- Matthewman G., Lee A., Kaur J.G., Daley A.J. Physical activity for primary dysmenorrhea: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018 Sep. 219(3). 255. e1-255.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.04.001.
- Fernández-Martínez E., Abreu-Sánchez A., Velarde-García J.F., Iglesias-López M.T., Pérez-Corrales J., Palacios-Ceña D. Living with Restrictions. The Perspective of Nursing Students with Primary Dysmenorrhea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020. 17(22). 8527. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/ijerph17228527
- Burnett M., Lemyre M. No. 345-Primary Dysmenorrhea Consensus Guideline. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2017 Jul. 39(7). 585-595. doi: 10.1016/j.jogc.2016.12.023.
- Bajalan Z., Moafi F., MoradiBaglooei M., Alimoradi Z. Mental health and primary dysmenorrhea: a systematic review. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019 Sep. 40(3). 185-194. doi: 10.1080/0167482X.2018.1470619.
- Li A.D., Bellis E.K., Girling J.E., Jayasinghe Y.L., Grover S.R., Marino J.L., Peate M. Unmet Needs and Experiences of Adolescent Girls with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding and Dysmenorrhea: A Qualitative Study. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2020 Jun. 33(3). 278-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2019.11.007.
- Rafique N., Al-Sheikh M.H. Prevalence of primary dysmenorrhea and its relationship with body mass index. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2018 Sep. 44(9). 1773-1778. doi: 10.1111/jog.13697.
- Ryan S.A. The Treatment of Dysmenorrhea. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2017 Apr. 64(2). 331-342. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2016.11.004.
- Heskes A.M., Sundram T.C.M., Boughton B.A., Jensen N.B., Hansen N.L., Crocoll C., Cozzi F. et al. Biosynthesis of bioactive diterpenoids in the medicinal plant Vitex agnus-castus. Plant. J. 2018 Mar. 93(5). 943-958. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13822.
- Sogame M., Naraki Y., Sasaki T., Seki M., Yokota K., Masada S., Hakamatsuka T. Quality Assessment of Medicinal Product and Dietary Supplements Containing Vitex agnus-castus by HPLC Fingerprint and Quantitative Analyses. Chem. Pharm. Bull (Tokyo). 2019. 67(6). 527-533. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c18-00725.
- Vo Q.V., Mechler A. In Silico Study of the Radical Scavenging Activities of Natural Indole-3-Carbinols. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020 Jan 27. 60(1). 316-321. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00917.
- Escobar L.K. Two new species of Passsiflora (Passifloraceae) from Northern South America. Phytologia. 2019. 69. 364-367. doi: 10.5962/bhl.part.9803.
- Rolland A., Fleurentin J., Lanhers M.C., Misslin R., Mortier F. Neurophysiological effects of an extract of Eschscholzia californica Cham. (Papaveraceae). Phytother. Res. 2001 Aug. 15(5). 377-81. doi: 10.1002/ptr.884.
- Semenyna H.B., Shatylovych K.L., Fartushok T.V. A new approach to the combination therapy of polycystic ovary syndrome. World of Medicine and Biology. 2020. 2(72). 125-129. doi: 10.26724/2079-8334-2020-2-72-125-129.

/25.jpg)