Вступ
Незважаючи на великі успіхи, досягнуті в дитячій гастроентерології, проблема захворювань органів травлення у дітей залишається досить актуальною у зв’язку зі значною поширеністю, а також зміною феноменології в сучасних умовах [1]. Хвороби шлунково-кишкового тракту займають у даний час друге місце у структурі загальної захворюваності дітей, поступаючись лише патології бронхолегеневої системи. Більшість дитячих гастроентерологів відзначають наявність феномена «айсберга» при захворюваннях шлунково-кишкового тракту, коли більше половини хворих, які мають ознаки даної патології, не звертаються за медичною допомогою і їм не встановлюється своєчасно діагноз [2].
На сьогодні добре відомо, що виразка дванадцятипалої кишки (ВДПК) розглядається як хронічне рецидивуюче захворювання, що характеризується формуванням виразкового дефекту у дванадцятипалій кишці (ДПК) на тлі запальних змін слизової оболонки шлунка і ДПК, схильне до прогресування, із залученням у патологічний процес інших органів і систем, розвитком ускладнень, що загрожують життю хворого. Все це призводить до значного зниження якості життя хворих [3], збільшення інвалідизації дитячого, а в подальшому і дорослого населення [4, 5]. Крім того, проблема в даний час виходить за рамки гастроентерології та вимагає уваги лікарів інших спеціальностей: ендокринологів, неврологів, кардіологів, пульмонологів, отоларингологів, хірургів і навіть онкологів. Це пов’язано перш за все з наявністю безлічі атипових симптомів і супутніх хвороб, патогенетично пов’язаних із кислотозалежними захворюваннями. В етіології ВДПК значиму роль відіграє інфікування слизової оболонки Helicobacter pylori (Н.руlori). Феномен запалення в слизовій оболонці шлунка не тільки універсальний для всіх клінічних форм, асоційованих із хелікобактерною інфекцією, але й специфічний, оскільки такий вид дифузного запального процесу в даній екологічній ніші не здатний викликати жоден інший збудник [6]. Характерною особливістю Н.руlori-індукованого запалення є масивна нейтрофільна інфільтрація слизової [7, 8]. Нейтрофіли — дуже рухливі клітини, що мають швидку реакцію на хемотаксичні й активаційні стимули. Зазвичай вони рекрутуються з кровотоку в тканини на ранніх стадіях інфекції і першими зустрічають антигени, які проникли через захисні механізми організму [9, 10]. Макрофаги з’являються в більш пізній час. Той факт, що при Н.pylori-інфікуванні нейтрофіли протягом тривалого часу перевершують чисельністю макрофаги, дозволив припустити наявність Н.pylori-індукованого стану особливого типу, так званого хронічного гострого запалення [11–14]. У зв’язку з тим, що Н.pylori-інфекція індукує значну нейтрофільну інфільтрацію, було припущено, що Н.pylori-індуковані пошкодження є нейтрофілопосередкованими [15, 16]. Підтвердженням цього зв’язку є спостереження, що великі пошкодження слизової пов’язані з тяжкістю Н.pylori-інфекції та нейтрофільною інфільтрацією.
Мета дослідження: вивчити динаміку запальних змін слизової оболонки у дітей із ВДПК.
Матеріали та методи
Групу спостереження становили 106 дітей віком від 10 до 18 років із верифікованою ВДПК, які знаходилися на стаціонарному лікуванні в гастроентерологічних відділеннях Чернівецької обласної та міської дитячих лікарень. Для верифікації діагнозу всім дітям проводили фіброезофагогастродуоденоскопію (ФЕГДС), внутрішньошлункову рН-метрію, серологічне (з метою виявлення інфікування Н.pylori) та морфологічне дослідження (матеріал забирали з антрального відділу шлунка). Гастробіоптати фіксували у 10% нейтральному забуферованому формаліні з подальшою заливкою в парафін. Депарафінізовані серійні зрізи забарвлювали гематоксиліном та еозином. Забарвлені препарати вивчали під мікроскопом (об’єктив × 90, окуляр × 10). Морфологічну оцінку стану слизової оболонки антрального відділу шлунка здійснювали за схемою: висота і форма поверхневого й залозистого епітелію; наявність ознак дистрофії і проліферації; вміст просвіту залоз; клітинна інфільтрація і її характер; наявність набряку. Результати дослідження трактували за сіднейською системою [17]. Критеріями включення були наявність патології верхніх відділів шлунково-кишкового тракту (хронічний гастрит, хронічний гастродуоденіт, виразка дванадцятипалої кишки). Діагноз встановлювався відповідно до критеріїв діагностики уніфікованого протоколу надання медичної допомоги дітям (наказ МОЗ України від 29.01.2013 року). У всіх пацієнтів отримана інформована згода. Статистичну обробку результатів проведено з використанням стандартних пакетів програм Microsoft Excel. Для кожної групи досліджень, які мали нормальний розподіл, вираховували середню арифметичну величину (М) та похибку середньої арифметичної (m) (M ± m). Якісні показники наводили у вигляді абсолютних значень та частки (у відсотках) від загальної кількості за вибіркою чи у групі. Оцінка вірогідності здійснювалася за допомогою критерію Стьюдента (t). Різниця вважалася вірогідною при р < 0,05.
Результати та обговорення
Проведений генеалогічний аналіз виявив, що у 39,6 % (42 дітей) спостережень матері пацієнтів страждали від гастроентерологічної патології, у 26,6 % (29 дітей) — батьки. Серед родичів другого ступеня споріднення по жіночій лінії захворювання травного тракту відзначали у 20,7 % (22 дітей) випадків, по чоловічій лінії — у 16,9 % (19 дітей).
При проведенні ендоскопічного дослідження у 49,1 % дітей діагностували порушення моторно-евакуаторної функції у вигляді дуоденогастрального і/або гастроезофагеального рефлюксів. Серед порушень моторно-евакуаторної функції вірогідно частіше виявляли дуоденогастральний (30,1 %), ніж гастроезофагеальний (18,7 %), рефлюкс.
Дослідження на H.pylori встановило позитивний результат у 81,1 % дітей із ВДПК. За результатами ФЕГДС було встановлено, що у дітей із ВДПК переважали еритематозні зміни слизової оболонки шлунка та дванадцятипалої кишки. Гіпертрофічна гастропатія у поєднанні з еритематозними змінами ДПК була відмічена у 16,9 % дітей. Ерозивні зміни слизової оболонки шлунка були виявлені у 21,3 %. У переважної більшості хворих дітей (92,4 % ) діагностували хронічний неатрофічний гастрит та/або гастродуоденіт із різним ступенем вираженості запального процесу (рис. 1), у 7,6 % дітей — хронічний атрофічний гастрит.
В антральному відділі шлунка були відмічені порушення рельєфу слизової оболонки у вигляді вкорочення ямок і сплощення валиків, явища периваскулярного набряку, повнокров’я судин. Більш виражені відхилення реєструвалися в дітей із ВДПК, асоційованою з H.pylori, з переважанням помірних і виражених запальних змін слизової оболонки шлунка. Це свідчить про те, що інфікування даним збудником може посилювати запальні зміни у слизовій оболонці шлунка.
/36.jpg)
Морфологічне дослідження виявило в усіх випадках ознаки катарального гастриту. Встановлено зниження висоти поверхневого епітелію, яка в середньому становила 15,1 ± 8,3 мкм. У 67,9 % обстежених встановлено ознаки десквамації поверхневого епітелію. Середня висота залозистого епітелію становила 23,9 ± 5,7 мкм. Нормальна форма епітелію реєструвалася у більшості випадків (67,8 %). Варто зауважити, що у 72,3 % зразків в епітеліальних клітинах характерним був розвиток зернистої дистрофії, однак при цьому траплялася незначна кількість клітин із ознаками балонної дистрофії і некрозу. Нейтрофільна інфільтрація слизової оболонки була відзначена у 6,9 % пацієнтів без інфікування Н.pylori та у 57,5 % інфікованих Н.pylori. Проліферативні зміни залозистого епітелію встановлені у 45,2 % випадків. Порушення мікроциркуляції у вигляді крововиливів і мікротромбозів були діагностовані у 56,6 % випадків.
Повторне ендоскопічне та морфологічне дослідження було проведено через 3 місяці після лікування. Кількість позитивних випадків діагностики Н.pylori становила 30,1 %. Привертало увагу збільшення кількості пацієнтів із ознаками езофагіту (у 7,5 % дітей реєструвалися ендоскопічні ознаки езофагіту 2-го ступеня, у 12,3 % — 1-го ступеня). Частка випадків дуоденогастрального рефлюксу збільшилася на 2,8 % і становила 34,9 %.
Частота виявлення в препаратах пластів циліндричного епітелію і його проліферації в динаміці практично не змінювалася. Клітинна інфільтрація була представлена нейтрофілами і лімфоцитами. Середня кількість лімфоцитів знижувалася в неінфікованих H.pylori з 71,6 до 33,9 % випадків, у інфікованих H.pylori — майже не змінювалася. Варто відзначити значне зниження кількості нейтрофілів після антихелікобактерної терапії у пацієнтів із H.pylori-інфекцією (рис. 2).
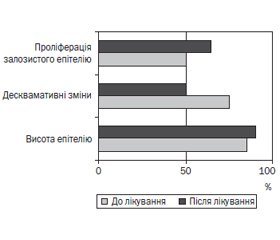
Морфологічні зміни в біоптатах слизової оболонки антрального відділу шлунка наведені на рис. 3.
Аналіз морфологічних вимірювань показав, що висота поверхневого епітелію порівняно з даними первинного обстеження знижувалася на 3,5 мкм (з 15,1 ± 8,3 мкм до 11,6 ± 4,9 мкм). Частота десквамативних змін епітелію зменшувалася на 22,7 %, а проліферація залозистого епітелію підвищувалася на 12,4 %.
Висновки
1. При морфологічному дослідженні у більшості дітей був діагностований хронічний неатрофічний гастрит із помірним ступенем запалення слизової оболонки.
2. Морфологічні зміни в біоптатах слизової оболонки шлунка відрізняються залежно від наявності інфекції H.pylori та зберігаються через 3 місяці після проведеного лікування.
Конфлікт інтересів. Автори заявляють про відсутність конфлікту інтересів при підготовці даної статті та дотримання принципів конфіденційності, концепції інформованої згоди та урахування основних положень GCР ІCH та Гельсінської декларації з біомедичних досліджень.
Отримано/Received 29.04.2021
Рецензовано/Revised 11.05.2021
Прийнято до друку/Accepted 20.05.2021
Список литературы
1. Степанов Ю.М., Скирда І.Ю., Петішко О.П. Хвороби органів травлення — актуальна проблема клінічної медицини. Гастроентерологія. 2019. 53(1). 1-6. doi: 10.22141/2308-097.53.1.2019.163450.
2. Шекера О.Г., Мельник Д.В. Поширеність серед дітей хвороб органів травлення та виразкової хвороби дванадцятипалої кишки — актуальна проблема сімейної медицини. Сімейна медицина. 2017. 1(69). 16-20.
3. Мельник Д.В. Виразкова хвороба дванадцятипалої кишки у дітей шкільного віку (огляд літератури). Сімейна медицина. 2018. 3(77). 125-129.
4. Тищенко Д.В., Матвеева О.В., Черненков Ю.В., Маслякова Г.Н., Бучарская А.Б. Клинико-морфологическое исследование хронического дуоденита у детей. Саратовский научно-медицинский журнал. 2012. Т. 8. № 3. 799-803.
5. Боброва В.І., Воробієнко Ю.І., Кошова А.О. Морфо-функціональні особливості хронічної гастродуоденальної патології у дітей, які палять. Междунар. журн. педиатрии, акушерства и гинекол. 2013. 4(2). 34-38.
6. Baj J., Forma A., Sitarz M. et al. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors-Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenicity in the Gastric Microenvironment. Cells. 2020. 10(1). 27. doi: 10.3390/cells10010027.
7. Burkitt M.D., Duckworth C.A., Williams J.M., Pritchard D.M. Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric pathology: insights from in vivo and ex vivo models. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017. 10(2). 89-104. doi: 10.1242/dmm.027649.
8. Bertaux-Skeirik N., Feng R., Schumacher M.A. et al. CD44 plays a functional role in Helicobacter pylori-induced epithelial cell proliferation. PLoS Pathog. 2015. 11(2). Е1004663. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004663.
9. Panarese A., Galatola G., Armentano R. et al. Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation masks the underlying presence of low-grade dysplasia on gastric lesions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020. 26(26). 3834-3850. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i26.3834.
10. Mera R.M., Bravo L.E., Camargo M.C. et al. Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori infection as a determinant of progression of gastric precancerous lesions: 16-year follow-up of an eradication trial. Gut. 2018. 67. 1239-1246.
11. Panarese A., Shahini E., Pesce F., Caruso M.L. Detection of lesions in Helicobacter Pylori gastritis before and after eradication by expert endoscopists. UEG J. 2018. 6. A734.
12. Gonciarz W., Krupa A., Hinc K. et al. The effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and different H. pylori components on the proliferation and apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells and fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2019. 14(8). Е0220636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220636.
13. Gobert A.P., Wilson K.T. Human and Helicobacter pylori Interactions Determine the Outcome of Gastric Diseases. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017. 400. 27-52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50520-6_2.
14. Sgouras D.N., Trang T.T., Yamaoka Y. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter. 2015. 20(1). 8-16. doi: 10.1111/hel.12251/.
15. Sun H., Yuan H., Tan R. et al. Immunodominant antigens that induce Th1 and Th17 responses protect mice against Helicobacter pylori infection. Oncotarget. 2018. 9(15). 12050-12063. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23927.
16. Joo M. Rare Gastric Lesions Associated with Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Histopathological Review. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2017. 51(4). 341-351. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2017.04.03.
17. Dixon M.F., Genta R.M., Yardley J.H., Correa P. Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, Houston 1994. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996. 20. 1161-1181.
/36.jpg)

/37.jpg)