Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №2, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Цукровий діабет і артеріальна гіпертензія
Авторы: Сергієнко В.О., Сергієнко О.О.
Львівський національний медичний університет імені Данила Галицького, м. Львів, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
В огляді проведений аналіз літературних джерел, присвячених сучасному стану проблеми цукрового діабету (ЦД) і артеріальної гіпертензії (АГ). За даними Всесвітньої організації охорони здоров’я, АГ та ЦД 2-го типу після ожиріння є одними з провідних чинників серцево-судинного ризику, які найбільш поширені серед населення світу. За останні 30 років поширеність АГ зменшилась до однієї четвертої частини населення світу, але захворюваність на ЦД зросла з 4,7 до 8,5 %, і прогноз на майбутнє свідчить про подальший драматичний приріст. Покращення обізнаності, лікування та контролю цих захворювань є основною метою глобальної системи охорони здоров’я. Поширеність АГ у хворих на ЦД 2-го типу до трьох разів вища, ніж у пацієнтів без ЦД, а поєднання АГ і ЦД суттєво збільшує ймовірність розвитку серцево-судинних захворювань. Несприятливий взаємозв’язок цих двох станів, прискорюючи процеси атеросклерозу, може спричинити негативні патофізіологічні зміни серцево-судинної системи. Крім того, відомо, що кардіоваскулярна автономна нейропатія, яка виникає в результаті пошкодження вегетативних нервових волокон, що іннервують серце та судини, є вагомим ускладненням ЦД 2-го типу, особливо за наявності системної АГ. Зокрема, аналізуються питання, пов’язані із спільними патофізіологічними механізмами, основними системними та метаболічними чинниками, що можуть сприяти коморбідності ЦД і АГ. Наведені класифікація, особливості діагностики АГ, особливості оцінки ураження органів, опосередкованого АГ. Аналізуються питання, пов’язані з основними підходами до лікування артеріальної гіпертензії при цукровому діабеті; використанням блокаторів ренін-ангіотензинової системи, блокаторів кальцієвих каналів, тіазидних і тіазидоподібних діуретиків, блокаторів бета-адренергічних рецепторів, альфа-адреноблокаторів, антагоністів мінералокортикоїдних рецепторів; особливостями комбінованої терапії та лікування резистентної артеріальної гіпертензії.
This review article summarizes the existing literature on the current state of the problem of diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension. According to the World Health Organization, hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus, after obesity, are among the leading cardiovascular risk factors that are most common among the world’s population. Over the past 30 years, the prevalence of hypertension has decreased to a quarter of the world’s population, but the incidence of diabetes mellitus has increased from 4.7 to 8.5 %, and the forecast for the future indicates a further dramatic increase. Improving awareness, treatment and control of these diseases is a major goal of the global health system. The prevalence of hypertension in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is up to three times higher than in patients without diabetes mellitus, and the combination of hypertension and diabetes mellitus significantly increases the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease. The unfavorable relationship between these two conditions, accelerating the processes of atherosclerosis, can cause negative pathophysiological changes in the cardiovascular system. Also, it is known that cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, resulting from damage to the autonomic nerve fibers that innervate the heart and blood vessels, is a significant complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus, especially in the presence of systemic hypertension. In particular, the issues related to common pathophysiological mechanisms, main systemic and metabolic factors that may contribute to the development of diabetes mellitus and hypertension comorbidity are analyzed. Classification, features of diagnosis of arterial hypertension, assessment of the disorders of the organs mediated by arterial hypertension are presented. Issues related to the main approaches of arterial hypertension treatment in diabetes mellitus are analyzed, namely prescription of the inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system, calcium channel blockers, thiazide, and thiazide-like diuretics, beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists, alpha-blockers, mineralocorticoid-receptor antagonists as well as the features of combined therapy and treatment of resistant arterial hypertension.
цукровий діабет; артеріальна гіпертензія; огляд
diabetes mellitus; arterial hypertension; review
Класифікація артеріальної гіпертензії
Діагностика артеріальної гіпертензії
Особливості оцінки ураження органів, опосередкованого артеріальною гіпертензією
Лікування артеріальної гіпертензії при цукровому діабеті
Раціональне харчування та фізична активність
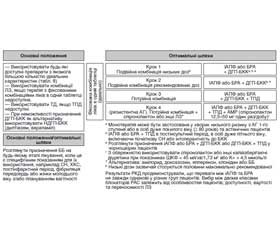
Основні положення лікування АГ у хворих на цукровий діабет [24, 31, 42–46]
Блокатори ренін-ангіотензинової системи
Блокатори кальцієвих каналів
Тіазидні й тіазидоподібні діуретики
Блокатори бета-адренергічних рецепторів
Препарати четвертої лінії в лікуванні АГ
Альфа-адреноблокатори
Резистентна АГ
Антагоністи мінералокортикоїдних рецепторів (антагоністи альдостерону)
Комбінована терапія
- IDF Diabetes Atlas (International Diabetes Federation website). 2020. Available from: https://www.idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabetes-atlas/134-idf-diabetes-atlas-8th-edition.html. Accessed 06/28/2020.
- Roth G.A., Huffman M.D., Moran A.E., Feigin V., Mensah G.A., Naghavi M., Murray C.J.L. Global and regional patterns in cardiovascular mortality from 1990 to 2013. Circulation. 2015. 132. 1667-78. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.008720.
- Zhou B., Bentham J., Di Cesare M., Bixby H., Danaei G., Cowan M.J., Paciorek C.J. et al. Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: a pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 191 million participants. Lancet. 2017. 389(10064). 37-55. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31919-5.
- NICE 2019. Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management. Available from: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng136.
- Lin J., Thompson T.J., Cheng Y.J., Zhuo X., Zhang P., Gregg E., Rolka D.B. Projection of the future diabetes burden in the United States through 2060. Popul. Health Metr. 2018. 16(1). 9. doi: 10.1186/s12963-018-0166-4.
- Muntner P., Einhorn P.T., Cushman W.C., Whelton P.K., Bello N.A., Drawz P.E., Green B.B. et al. Blood pressure assessment in adults in clinical practice and clinic-based research: JACC scientific expert panel. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019. 73(3). 317-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.069.
- Colussi G., Da Porto A., Cavarape A. Hypertension and type 2 diabetes: lights and shadows about causality. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2020. 34(2). 91-3. doi: 10.1038/s41371-019-0268-x.
- Lastra G., Syed S., Kurukulasuriya L.R., Manrique C., Sowers J.R. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: an update. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2014. 43(1). 103-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.09.005.
- Savoia C., Touyz R.M. Hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and excess cardiovascular risk: importance of baseline systolic blood pressure. Hypertension. 2017. 70(5). 882-3. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09764.
- Carthy E.R. Autonomic dysfunction in essential hypertension: a systematic review. Ann. Med. Surg. (Lond). 2013. 3(1). 2-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2013.11.002.
- Bassi D., Cabiddu R., Mendes R.G., Tossini N., Arakelian V.M., Caruso F.C.R., Bonjorno Júnior J.C. et al. Effects of сoexistence hypertension and type II diabetes on heart rate variability and cardiorespiratory fitness. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2018. 111(1). 64-72. doi: 10.5935/abc.20180105.
- Mori H., Saito I., Eguchi E., Maruyama K., Kato T., Tanigawa T. Heart rate variability and blood pressure among Japanese men and women: a community-based cross-sectional study. Hypertens. Res. 2014. 37(8). 779-84. doi: 10.1038/hr.2014.73.
- Amiya E., Watanabe M., Komuro I. The relationship between vascular function and the autonomic nervous system. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2014. 7(2). 109-19. doi: 10.3400/avd.ra.14-00048.
- Dong J.G. The role of heart rate variability in sports physiology. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016. 11(5). 1531-6. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3104.
- Arroyo-Carmona R.E., López-Serrano A.L., Albarado-Ibañez A., Mendoza-Lucero F.M., Medel-Cajica D., López-Mayorga R.M. et al. Heart rate variability as early biomarker for the evaluation of diabetes mellitus progress. J. Diabetes Res. 2016. 2016. 8483537. doi: 10.1155/2016/8483537.
- Jin L., Min G., Wei C., Min H., Jie Z. Exercise training on chronotropic response and exercise capacity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017. 13(3). 899-904. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4084.
- Petrie J.R., Guzik T.J., Touyz R.M. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: clinical insights and vascular mechanisms. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018. 34(5). 575-84. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2017.12.005.
- Sun D., Zhou T., Heianza Y., Li X., Fan M., Fonseca V.A., Qi L. Type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019.124(6). 930-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314487.
- Tsimihodimos V., Gonzalez-Villalpando C., Meigs J.B., Ferrannini E. Hypertension and diabetes mellitus: coprediction and time trajectories. Hypertension. 2018. 71(3). 422-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10546.
- Sowers J.R. Diabetes mellitus and vascular disease. Hypertension. 2013. 61(5). 943-7. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00612.
- Khangura D., Hong J., Kurukulasuriya R., Sowers J.R. Diabetes and hypertension. In: Saldaña J.R., ed. Diabetes Textbook: Clinical Principles, Patient Management and Public Health Issues. Basel: Springer, Cham. Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2019. 37. 573-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11815-0_37.
- Poulter N.R., Castillo R., Charchar F.J., Schlaich M.P., Schutte A.E., Tomaszewski M., Touyz R.M. et al. Are the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology high blood pressure guidelines fit for global purpose? Thoughts from the International Society of Hypertension. Hypertension. 2018. 72. 260-2. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11452.
- Williams B., Mancia G., Spiering W., Rosei E.A., Azizi M., Burnier M., Clement D.L. et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Europ. Heart J. 2018. 39(33). 3021-104. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339.
- Unger T., Borghi C., Charchar F., Khan N.A., Poulter N.R., Prabhakaran D., Ramirez A. et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2020. 75 (6). 1334-57. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15026.
- Valenza G., Citi L., Garcia R.G., Taylor J.N., Toschi N., Barbieri R. Complexity variability assessment of nonlinear time-varying cardiovascular control. Sci. Rep. 2017. 7. 42779. doi: 10.1038/srep42779.
- Stergiou G.S., O’Brien E., Myers M., Palatini P., Parati G., Kollias A., Birmpas D. et al.; STRIDE BP Scientific Advisory Board. STRIDE BP international initiative for accurate blood pressure measurement: Systematic review of published validation studies of blood pressure measuring devices. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich). 2019. 21(11). 1616-22. doi: 10.1111/jch.13710.
- Stergiou G.S., Palatini P., Modesti P.A., Asayama K., Asmar R., Bilo G., de la Sierra A. et al. Seasonal variation in blood pressure: Evidence, consensus and recommendations for clinical practice. Consensus statement by the European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring and Cardiovascular Variability. J. Hypertens. 2020. 38(7). 1235-43. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002341.
- Serhiyenko V.A., Serhiyenko L.M., Serhiyenko A.A. Recent advances in the treatment of neuropathies in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: focus on benfotiamine (review and own data). In: Berhardt L.V., ed. Advances in Medicine and Biology (Numbered series). New York: Nova Science Publishers, 2020. 166. Ch. 1. 1-80.
- Vinik A.I., Casellini C., Parson H.K., Colberg S.R., Nevoret M.L. Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes: A Predictor of Cardiometabolic Events. Front Neurosci. 2018 Aug 27. 12. 591. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00591.
- Rabi D.M., McBrien K.A., Sapir-Pichhadze R., Nakhla M., Ahmed S.B., Dumanski S.M., Butalia S. et al. Hypertension Canada’s 2020 Comprehensive Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis, Risk Assessment, and Treatment of Hypertension in Adults and Children. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020. 36(5). 596-624. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2020.02.086.
- Dedov I.I., Shestakova M.V., Mayorov A.Y., Vikulova O.K., Galstyan G.R., Kuraeva T.L., Peterkova V.A. et al. Standards of specialized diabetes care. 9th ed. Diabetes mellitus. 2019. 22(1S1). 1-144. doi: 10.14341/DM221S1. (In Russian).
- He F.J, Li J., Macgregor G.A. Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ. 2013. 346. f1325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f1325.
- Gay H.C., Rao S.G., Vaccarino V., Ali M.K. Effects of different dietary interventions on blood pressure: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertension. 2016. 67(4). 733-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06853.
- Cicero A.F.G., Grassi D., Tocci G., Galletti F., Borghi C., Ferri C. Nutrients and nutraceuticals for the management of high normal blood pressure: an evidence-based consensus document. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2019. 26(1). 9-25. doi: 10.1007/s40292-018-0296-6.
- Xie C., Cui L., Zhu J., Wang K., Sun N., Sun C. Coffee consumption and risk of hypertension: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2018. 32(2). 83-93. doi: 10.1038/s41371-017-0007-0.
- Roerecke M., Kaczorowski J., Tobe S.W., Gmel G., Hasan O.S.M., Rehm J. The effect of a reduction in alcohol consumption on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health. 2017. 2(2). e108-e20. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(17)30003-8.
- Global Burden of Disease Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017. 390(10100). 1345-422. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32366-8.
- Costa E.C., Hay J.L., Kehler D.S., Boreskie K.F., Arora R.C., Umpierre D., Szwajcer A. et al. Effects of high-intensity interval training versus moderate-intensity continuous training on blood pressure in adults with pre- to established hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Sports Med. 2018. 48(9). 2127-42. doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-0944-y.
- López A.L.S. Effectiveness of the mindfulness-based stress reduction program on blood pressure: a systematic review of literature. Worldviews Evid. Based Nurs. 2018. 15(5). 344-52. doi: 10.1111/wvn.12319.
- Wang J., Xiong X. Evidence-based Chinese medicine for hypertension. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013. 2013. 978398. doi: 10.1155/2013/978398.
- Liwa A.C., Smart L.R., Frumkin A., Epstein H.A., Fitzgerald D.W., Peck R.N. Traditional herbal medicine use among hypertensive patients in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014. 16(6). 437. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0437-9.
- Emdin C.A., Rahimi K., Neal B., Callender T., Perkovic V., Patel A. Blood pressure lowering in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2015. 313(6). 603-15. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.18574.
- de Boer I.H., Bangalore S., Benetos A., Davis A.M., Michos E.D., Muntner P., Rossing P. et al. Diabetes and Hypertension: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2017. 40. 1273-84. doi: 10.2337/dci17-0026.
- Whelton P.K., Carey R.M., Aronow W.S., Casey D.E., Collins K.J., Himmelfarb D., DePalma C. et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Forse on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018. 71. 1269-324. doi: 10.1161/HYP.00000000000000066.
- Mooradian A.D. Diabetes and atherogenic dyslipidemia. In: Saldaña J.R., ed. Diabetes Textbook: Clinical Principles, Patient Management and Public Health Issues. Basel: Springer, Cham. Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2019. 38. 587-96. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11815-0_38.
- American Diabetes Association. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. Diabetes Care. 2020. 43(Suppl. 1). S111-S34. doi: 10.2337/dc20-S010.
- Bando H. Recommended management of hypertensive patients with diabetes for renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors. Diab. Res. Open Access. 2020. 2(1). 4-8. doi: 10.36502/2020/droa.6161.
- Haneda M., Noda M., Origasa H., Noto H., Yabe D., Fujita Y., Goto A., Kondo T., Araki E. Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes 2016. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018. 9(3). 657-97. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12810.
- Bangalore S., Fakheri R., Toklu B., Messerli F.H. Diabetes mellitus as a compelling indication for use of renin angiotensin system blockers: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. BMJ. 2016. 352. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i438.
- Wright J.T. Jr., Williamson J.D., Whelton P.K., Snyder J.K., Sink K.M., Rocco M.V., Reboussin D.M. et al. SPRINT Research Group. A randomized trial of intensive versus standard blood pressure control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015. 373(22). 2103-16. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1511939.
- Serhiyenko A.A., Serhiyenko V.A. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: treatment. 2020. 16(8). 93-104. Mìžnarodnij endokrinologìčnij žurnal = International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.16.8.2020.222888.
- Palmer S.C., Mavridis D., Navarese E., Craig J.C., Tonelli M., Salanti G., Wiebe N. et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of blood pressure lowering agents in adults with diabetes and kidney disease: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2015. 385(9982). 2047-56. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62459-4.
- Catala-Lopez F., Macias Saint-Gerons D., Gonzalez-Bermejo D., Rosano G.M., Davis B.R., Ridao M., Zaragoza A. et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes of renin-angiotensin system blockade in adult patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review with network meta-analyses. PLoS Med. 2016. 13(3). e1001971. doi: 10.1371/ journal.pmed.1001971.
- Parving H.H., Brenner B.M., McMurray J.J.V., de Zeeuw D., Haffner S.M., Solomon S.D., Chaturvedi N. et al. Cardiorenal end 4129 points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012. 367(23). 2204-13. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1208799.
- Mancia G., Schumacher H., Redon J., Verdecchia P., Schmieder R., Jennings G., Yusoff K. et al. Blood pressure targets recommended by guidelines and incidence of cardiovascular and renal events in the Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination With Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial (ONTARGET). Circulation. 2011. 124(16). 1727-36. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.008870.
- Koval S.M., Yushko K.O., Snihurska I.O., Starchenko T.G., Pankiv V.I., Lytvynova O.M., Mysnychenko O.V. Relations of angiotensin-(1-7) with hemodynamic and cardiac structural and functional parameters in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Arterial Hypertension (Poland). 2019. 23(3).183-189. doi: 10.5603/AH.a2019.0012.
- Iliescu R., Lohmeier T.E., Tudorancea I., Laffin L., Bakris G.L. Renal denervation for the treatment of resistant hypertension: review and clinical perspective. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2015. 309(7). F583-F94. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00246.2015.
- Bakris G.L., Pitt B., Weir M.R., Freeman M.W., Mayo M.R., Garza D., Stasiv Y. et al.; AMETHYST-DN Investigators. Effect of Patiromer on Serum Potassium Level in Patients With Hyperkalemia and Diabetic Kidney Disease: The AMETHYST-DN Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015. 314(2). 151-61. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.7446.
- Filippatos G., Anker S.D., Böhm M., Gheorghiade M., Køber L., Krum H., Maggioni A.P. et al. A randomized controlled study of finerenone vs. eplerenone in patients with worsening chronic heart failure and diabetes mellitus and/or chronic kidney disease. Eur. Heart J. 2016. 37. 2105-14. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw132.
- Tobe S.W., Gilbert R.E., Jones C., Leiter L.A., Prebtani A.P.H., Woo V. 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines. Treatment of Hypertension. Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Can. J. Diabetes. 2018. 42(Suppl. 1). S186-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2017.10.011.

/102.jpg)
/102_2.jpg)
/103.jpg)
/104.jpg)
/105.jpg)
/106.jpg)
/109.jpg)
/109_2.jpg)