Журнал «Травма» Том 17, №6, 2016
Вернуться к номеру
Методика рентгенологічного обстеження кульшових суглобів у пацієнтів із дитячим церебральним паралічем
Авторы: Голюк Є.Л.
ДУ «Інститут травматології та ортопедії НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
Проведено ретроспективний аналіз рентгенограм кульшових суглобів у пацієнтів із дитячим церебральним паралічем та встановлено, що коректна стандартизована укладка пацієнта при рентгенологічному обстеженні кульшових суглобів є визначальною умовою для подальшого динамічного спостереження за рентгеноморфометричними показниками кульшових суглобів та вибору правильної тактики лікування. Методика включає чотири етапи: визначення величини контрактури у кульшових суглобах за допомогою клінічного обстеження, коректну укладку пацієнта при проведенні рентгенологічного обстеження, оцінку рентгеноморфометричних показників коректності укладки, оцінку діагностичних рентгеноморфометричних критеріїв кульшових суглобів. У групі пацієнтів з некоректною укладкою помилкове визначення рентгеноморфометричних показників кульшових суглобів наближається до 100 %, в той час як при коректній укладці спостерігається протилежна ситуація.
Проведен ретроспективный анализ рентгенограмм тазобедренных суставов у пациентов с детским церебральным параличом и установлено, что корректная стандартизированная укладка пациента при рентгенологическом обследовании тазобедренных суставов является определяющим условием для дальнейшего динамического наблюдения по рентгеноморфометрическим показателям тазобедренных суставов и выбора правильной тактики лечения. Методика включает четыре этапа: определение величины контрактуры в тазобедренных суставах с помощью клинического обследования, корректную укладку пациента при проведении рентгенологического обследования, оценку рентгеноморфометрических показателей корректности укладки, оценку диагностических рентгеноморфометрических критериев тазобедренных суставов. В группе пациентов с некорректной укладкой ошибочное определение рентгеноморфометрических показателей тазобедренных суставов приближается к 100 %, в то время как при корректной укладке наблюдается обратная ситуация.
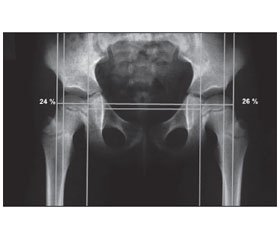
Background. X-ray indicators of the hip are important diagnostic factors of spastic hip dislocation in cerebral palsy. Correct X-ray examination has a decisive influence on the treatment strategy. Correct positioning parameters are well known, but their importance is often underestimated. This could be a trigger factor for further diagnostic and treatment errors. Materials and me-thods. The material was radiographs of the hip joints of 126 patients with cerebral palsy aged 2 to 18 years. Retrospective analysis of X-ray indicators of the hip in patients with cerebral palsy was performed, they were divided into 2 groups: 1) indicators to determine the correct positioning (the distance between the pubic symphysis and the tip of the coccyx, symmetry of obturator foramen, crossing of the anterior and posterior edge of the acetabulum); 2) diagnostic indicators (migration index, caput-collum-diaphyseal angle).
Results. The technique of X-ray examination of the hip in patients with cerebral palsy includes the following steps: determination of the hip contracture using clinical examination; correct positioning of a patient during radiological examination, taking into account the contracture in the hip; evaluation of correct X-ray indicators (distance «pubis — tip of the coccyx», symmetry of obturator foramen, determination of the crossing of anterior and posterior acetabular edge); evaluation of the shift of diagnostic X-ray criteria of the femoral neck-shaft angle, migration index. Conclusions. Correct X-ray examination of the hip in cerebral palsy is very important for further dynamic observation of X-ray indicators of the hip and choosing the right treatment. The method includes four steps: determination of the contracture in the hip using clinical examination, correct positioning of a patients during X-ray examination, evaluation of X-ray indicators for correct positioning, evaluation of diagnostic X-ray indicators.
рентгенограма; кульшовий суглоб; дитячий церебральний параліч; рентгеноморфометричні показники
рентгенограмма; тазобедренный сустав; детский церебральный паралич; рентгеноморфометрические показатели
X-ray pattern; hip joint; cerebral palsy; morphometric X-ray indicators
Статтю опубліковано на с. 31-36
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати та обговорення
Висновки
1. Consensus Statement on Hip Surveillancefor Children with Cerebral Palsy: Australian Standards of Care / M. Wynter, N. Gibson, M. Kentish [et al.] // Government of Western Australia, Department of health. — 2008. — 16 p.
2. Cornell M. The hip in cerebral palsy / M. Cornell // Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. — 1995. — V. 37 — P. 3-18.
3. Cooke P.H. Dislocation of the hip in cerebral palsy: natural history and predictability / P.H. Cooke, W.G. Cole, R.P. Carey // J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. — 1989. — V. 71. — P. 441-446.
4. Hip surveillance in children with cerebral palsy: Impact on the surgical management of spastic hip disease / F. Dobson, R.N. Boyd, J. Parrott [et al.] // J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. — 2002. — V. 84. — P. 720-726.
5. The ischial spine sign does pelvic tilt and rotation matter? / D. Kakaty, A. Fischer, H. Hosalkar [et al.] // Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. — 2010. — № 468. — Р. 769-774.
6. Estimation of pelvic tilt on anteroposterior X-rays — a comparison of six parameters / M. Tannast, S.B. Murphy, F. Langlotz [et al.] // Skeletal Radiol. — 2005.
7. A systematic approach to the plain radiographic evaluation of the young adult hip / J. Clohisy, J. Carlisle, P. Beaulé [et al.] // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. — 2008. — № 4. — Р. 47-66.
8. Wynter M., Gibson N., Kentish M. Consensus Statement on Hip Surveillancefor Children with Cerebral Palsy: Australian Standards of Care. Government of Western Australia, Department of health. 2008. — 16 p.
9. Cornell M. The hip in cerebral palsy // Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. — 1995. — V. 37. — Р. 3-18.
10. Cooke P.H., Cole W.G., Carey RP. Dislocation of the hip in cerebral palsy: natural history and predictability // J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. — 1989. — V. 71. — Р. 441-446.
11. Dobson F., Boyd R.N., Parrott J. Hip surveillance in children with cerebral palsy: Impact on the surgical management of spastic hip disease // J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. — 2002. — V. 84. — Р. 720-726.
12. Kakaty D.K., Fischer A.F., Hosalkar H.S., Siebenrock K.A., Tannast M. The Ischial Spine Sign: Does Pelvic Tilt and Rotation Matter? // Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. — 2010 Mar. — № 468(3). — Р. 769-774. — doi: 10.1007/s11999-009-1021-5.
13. Tannast M., Murphy S.B., Langlotz F., Anderson S.E., Siebenrock KA. Estimation of pelvic tilt on anteroposterior X-rays — a comparison of six parameters // Skeletal Radiol. — 2006 Mar. — № 35(3). — Р. 149-55.
14. Clohisy J.C., Carlisle J.C., Beaulé P.E., Kim Y.-J., Trousdale R.T., Sierra R.J., Leunig M., Schoenecker P.L., Millis M.B. A Systematic Approach to the Plain Radiographic Evaluation of the Young Adult Hip // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. — 2008 Nov 1. — № 90(Suppl. 4). — Р. 47-66. — doi: 10.2106/JBJS.H.00756.

/32.jpg)
/33.jpg)
/33_2.jpg)
/34.jpg)
/34_2.jpg)