Журнал «Травма» Том 16, №3, 2015
Вернуться к номеру
Comparative analysis of the stresses in the "bone-implant" system of the radial head arthroplasty with different design implants
Авторы: S.S.Strafun - Department of microsurgery and reconstructive surgery of the upper extremity SI “Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics of NAMS of Ukraine”, Kyiv, Ukraine; I.V. Boyko - SSI "SPC RMB" Minimally Invasive Surgery Center, Kyiv, Ukraine; V.B. Makarov - SI specialized medical unit number 6, Dnipropetrovsk, Ukraine; Scherbakov - Hospital at station Krivyi Rig, Ukraine; O.S. Radzhabov - Design Bureau, a design engineer, Kharkiv, Ukraine; О.S.Strafun - Department of microsurgery and reconstructive surgery of the upper extremity SI “Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics of NAMS of Ukraine”, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Introduction. Fractures of the head and neck of the radius make up to 1,7-5,4% of all fractures of bones of the human skeleton, and about 30% of injuries in the elbow joint. When polyfragmental fractures of the radial head occurs arthroplasty of the radial head is performed for restoration of stability of the elbow joint and length of the radius. Our objective was to compare the stress distribution in the "bone-implant" system after the radial head arthroplasty with prosthesis of different designs.
Materials and methods. We designed a geometric model of the elbow joint, and various models of radial head prosthesis. Based on the finite element model a numerical experiment was made.
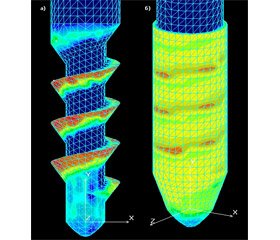
Results and discussion. We performed four series of calculations of the stress-strain state of the elbow under the influence of an axial load on the radial bone in the pronation-supination.
Conclusions:
1. The radial head has not strictly fixed radius of movement relative to the capitulum humeri at different angles of pronation-supination. Compliance with the articular surfaces in a healthy elbow is provided by intricate configuration of the radial head and capitulum humeri.
2. The use of monopolar implant increases the stresses in the bones of the elbow joint and the contact stress at the articular cartilage surfaces for 114 - 207%.
3. The use of the bipolar implant increases the stresses in the humerus and contact stresses at capitulum humeri for 44%.
4. Influence of the axial load on the radial bone with monopolar radial head implant during pronation-supination leads to increase of contact stresses in the bones of the elbow joint in two times. It is also increases moves of the radial head backward, which leads to the soft tissues covering the radial head stretchability.
5. The use of bipolar radial head implants shows a stable position of the prosthesis articular surface on the capitulum humeri and absence of stresses growth in the bone and the cartilage surface of the elbow joint in comparison with the healthy elbow joint.
6. Character of moving of the "floating" head of the bipolar prosthesis in a stable position for all the calculated values of the angle of rotation in pronation-supination demonstrates tendency for reducing of the distance between the contact surfaces of radius humerus and ulna. So, it can be assumed that under such loadings ligaments that cover the elbow joint, will not experience any additional load.
7. Stresses in the contact area of developed "floating" head prosthesis and humerus is not exceeding 3 MPa. This shows a large unloading of the elbow joint in relation to the stress that appear in the normal elbow.
8. Comparing the maximum stresses that appear in all calculated angles of rotation of the radius at the pronation-supination in normal and replaced by developed "floating" radial head prosthesis it was defined that stress load decreased by 45-60%.
9. Comparative analysis of stresses that appear in the "bone-implant" system in normal elbow joint and in substituted by developed unipolar prosthesis with a "floating" head revealed no overload, which can lead to destruction of the system, and also showed the absence of moments of forces that bring the system out of balance.
10. Proceeding from the above mentioned features of the contact of radius head with the capitulum humeri, when considering the choice of implant for the replacement of the radial head, preference should be given to the modular bipolar prosthesis with "floating head".